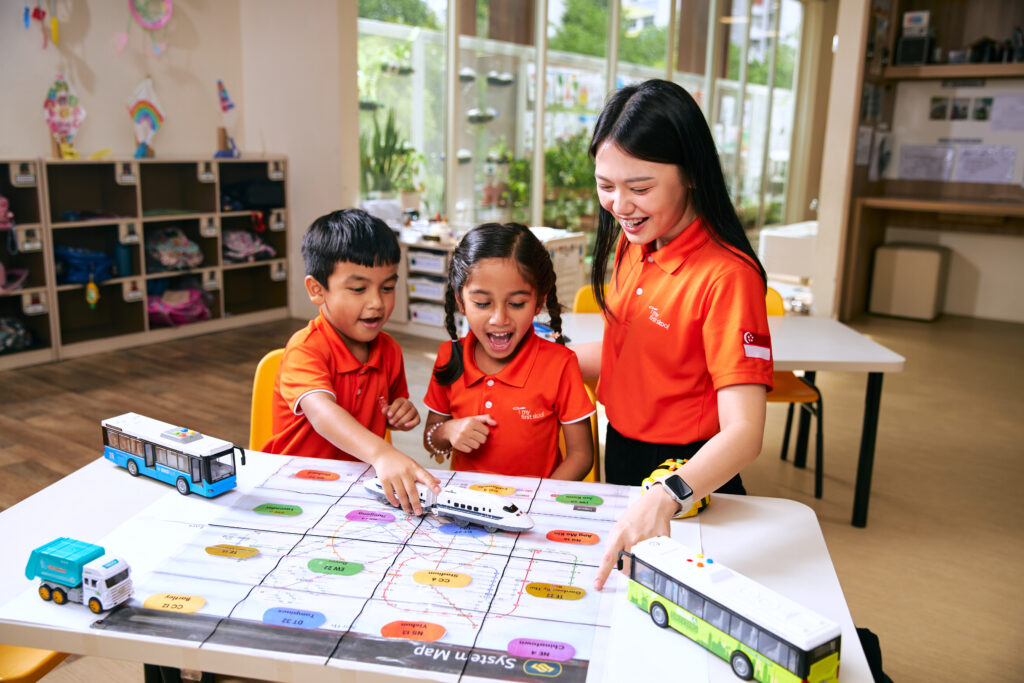
Safety in aviation depends on consistent compliance with rules and procedures. Even small lapses can have significant consequences, making training quality as important as technology. Recognizing that diverse learners require a pedagogical approach tailored to their needs, Sonoran Desert Institute (SDI), which is accredited by the Distance Education Accrediting Commission (DEAC), combines accredited instruction with accessible, strengths-based learning strategies in their uncrewed systems coursework.
By tailoring training to diverse learning styles, programs enhance safety outcomes throughout the industry. Neurodivergent trainees who excel with structure, checklists and pattern recognition contribute to habits that minimize human error, when given proper support. Inclusive instruction helps more students achieve academic success, while cultivating the reliability and discipline that aviation employers prioritize.
Linking Pedagogy to Compliance
Traditional instruction often relies on a one-size-fits-all approach, with lectures and textbooks taking center stage, leaving limited support for students who learn differently. Inclusive training models show that compliance is strengthened when rules are presented in multiple formats. By combining visual aids, simulations and hands-on practice, learners interact with material in ways that align with their strengths. This approach reduces frustration, boosts retention and helps students consistently grasp essential safety protocols. Compliance becomes a natural result of learning, rather than an obstacle.
Breaking down regulations into smaller modules, offering visual aids and allowing repeated practice help students internalize procedures. Learners who might struggle with abstract explanations gain clarity from concrete examples. In aviation, where every checklist must be followed exactly, this clarity translates directly into safer operations. Such structured support not only builds technical competence, but also instills the confidence needed to perform reliably under pressure.
The Role of Strengths-Based Approaches
Strength-based pedagogy flips the focus from accommodation to advantage. Rather than treating differences as deficits, instructors highlight abilities that fit the job. For instance, many autistic learners excel in attention to detail and pattern recognition, traits vital for reading sectional charts or monitoring drone telemetry. By showcasing these talents as assets, students feel empowered to pursue roles where their skills are indispensable. This approach also helps employers recognize the untapped potential of a diverse workforce, reframing inclusion as a driver of excellence. Strength-based pedagogy creates a pathway where learners thrive, industries benefit and training environments reflect real-world needs.
By leaning into these strengths early, programs build student confidence. That momentum carries forward to more complex topics, such as risk assessment, where attention and focus remain critical. The result is a workforce prepared not only to pass exams, but also to perform reliably under pressure. Reinforcing these foundational wins, students develop a stronger sense of mastery that encourages consistent effort. Each success not only validates their abilities, but also creates a positive feedback loop that sustains motivation. Over time, this approach transforms learning into a habit of disciplined focus, rather than a task of rote memorization.
Institutional Support
Colleges that focus on applied skills show that inclusive methods can uphold high standards. Sonoran Desert Institute incorporates strength-based instruction into their accredited online programs, linking regulatory knowledge with practical application. This approach illustrates how accessibility and compliance can coexist effectively.
Students benefit from modules designed with repetition, visuals and immediate feedback, while employers gain candidates trained to follow precise procedures. The model illustrates how educational institutions can address industry shortages by broadening access, while raising safety standards.
This dual advantage reinforces the link between classroom learning and real-world practice. By aligning training with employer expectations, institutions prepare students for both certification and the practical demands of high-stakes environments. The outcome is a talent pipeline that is more inclusive and dependable, providing industries with skilled professionals, while giving students meaningful, long-term careers.
Reducing Human Error
Human error remains the leading cause of aviation incidents. Training that anticipates different learning needs reduces this risk. Neurodivergent trainees, who might struggle in conventional classrooms, often thrive when instruction is structured around their strengths. Their reliability in following established routines adds a layer of protection against oversight.
Employers confirm that inclusive training produces workers who not only meet certification requirements, but also excel at maintaining discipline in real-world operations. By lowering the rate of mistakes, organizations reduce costs tied to accidents, delays and insurance claims. This consistency builds trust across teams, where every member can rely on colleagues to follow the same standards of accuracy and care. Over time, the culture of precision enhances organizational reputation and attracts partners who value reliability. In this way, inclusive training becomes not just a workforce strategy, but also a competitive advantage in demanding industries.
Building Trust with Data
Transparency is key to sustaining inclusive models. Programs that publish pass rates, retention numbers and employer satisfaction data build trust with both regulators and industry partners. When outcomes show that diverse learners meet or exceed national averages, skepticism fades.
This evidence-based approach positions inclusive training as a proven method for enhancing safety, rather than an experiment. Funders and policymakers respond more readily when measurable results are visible. Clear data demonstrates how training investments lead to fewer incidents and stronger compliance, helping secure long-term funding, and inform policies that prioritize both equity and safety. Consequently, inclusive training builds momentum as a sustainable solution adopted across industries.
Extending Benefits Beyond Aviation
Although this discussion centers on aviation, the lessons apply across skilled trades. Any field where safety and compliance matter can benefit from inclusive instruction. Industries, such as energy, construction and manufacturing, face similar challenges where human error carries real cost. By embracing diverse learning styles, these sectors can widen their talent pools, while strengthening compliance. Sonoran Desert Institute demonstrates the business case for this approach, showing how inclusion is not charity, but a strategy that improves outcomes for both workers and employers.
Aviation safety depends on more than technology. It relies on people trained to follow rules consistently. Inclusive training models strengthen compliance, by respecting different learning styles and building on individual strengths. This approach reduces human error and delivers the reliability that aviation demands. When pedagogy aligns with safety, both learners and industries gain.